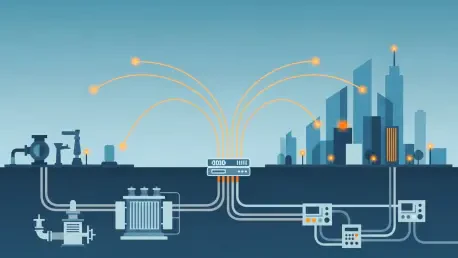
Serial device servers, a technology designed to connect legacy equipment with serial ports to modern Ethernet networks, are experiencing a surprising and robust resurgence that challenges the notion that newer is always better. Far from being relegated to the history books, this market is proving to be a critical enabler of global digital transformation, with a valuation of USD 287.45 million in 2024 that is projected to climb to an impressive USD 445.88 million by 2032. This sustained growth, advancing at a compound annual rate of 5.68%, is not driven by nostalgia but by the pragmatic and often unavoidable need to integrate older, yet perfectly functional, industrial machinery into today’s interconnected IT infrastructures. The success of this technology demonstrates a powerful lesson in innovation: sometimes the most effective path forward involves building a reliable bridge to the past rather than erasing it completely.
The Pragmatic Economics of Modernization
A primary force behind the continued relevance of serial device servers is the often-prohibitive cost associated with replacing entire industrial systems that are still performing their core functions effectively. Across essential sectors like manufacturing, energy, and transportation, a vast installed base of critical equipment—from CNC machines and PLCs to industrial sensors and control panels—continues to rely on proven serial communication protocols such as RS-232 and RS-485. Serial device servers offer a highly cost-effective and minimally disruptive solution, allowing organizations to extend the operational lifespan of these valuable legacy assets. This strategic approach circumvents the massive capital expenditure, prolonged downtime, and logistical complexities of a complete equipment overhaul, providing a practical pathway to modernization that preserves institutional knowledge and avoids interrupting established and efficient production lines.
This economic calculus is particularly evident in the large-scale modernization of public utilities and civic infrastructure, where budget constraints and the sheer scale of operations make wholesale replacement unfeasible. As governments and private enterprises invest heavily in building smart grids, intelligent traffic control networks, and automated utility monitoring systems, they confront the challenge of connecting countless legacy assets dispersed across vast geographical areas. Serial device servers have become a fundamental component in these ambitious initiatives, enabling secure remote control and real-time data acquisition from existing smart meters, electrical substation equipment, and traffic management systems. By doing so, they facilitate the creation of expansive, networked smart city ecosystems on a realistic budget, proving indispensable for turning futuristic urban concepts into present-day reality.
Enabling the Next Wave of Industrial Innovation
The widespread and accelerating adoption of Industry 4.0 principles stands as another major catalyst propelling the serial device server market forward. To successfully create the “smart factories” envisioned by this industrial revolution, manufacturers must be able to extract and analyze real-time data from every piece of machinery on the factory floor, including older but reliable controllers and actuators that lack native network connectivity. Serial device servers provide this essential link, acting as translators that convert serial data streams into a format compatible with modern IP-based control and monitoring systems, such as SCADA. This crucial connectivity is the bedrock for enhancing automation, enabling sophisticated predictive maintenance schedules to prevent failures before they happen, and ultimately reducing costly operational downtime—all of which are core tenets of the modern, data-driven industrial landscape.
Beyond the confines of the factory floor, the explosive proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the strategic shift toward edge computing have created an immense and growing demand for connecting a diverse array of remote devices. In these distributed ecosystems, serial device servers function as indispensable and reliable data gateways. They effectively link vast networks of industrial sensors, environmental monitors, agricultural equipment, and smart meters to centralized cloud platforms and localized edge computing nodes. This connectivity is absolutely critical for applications that depend on low-latency data processing and real-time analytics, from optimizing energy consumption in commercial buildings to managing remote resource extraction sites. By bridging this technological gap, serial device servers ensure that valuable data from legacy devices is not left behind in the race toward a more interconnected and intelligent world.
Navigating a Diverse and Security Conscious Landscape
As industrial systems become increasingly interconnected, the threat of cyberattacks has evolved into a paramount concern, especially for operators of critical infrastructure in sectors such as energy, water, and transportation. Modern serial device servers are engineered to directly address these vulnerabilities by incorporating an advanced suite of security features. By offering robust data encryption standards, secure user authentication protocols to prevent unauthorized access, and in some cases, FIPS-certified hardware, these devices create a hardened barrier against cyber threats. This focus on security ensures that the operational data transmitted from legacy equipment remains confidential and maintains its integrity as it traverses the network, making these servers a trusted and essential component in any strategy aimed at securing sensitive industrial operations from an ever-evolving landscape of digital risks.
The remarkable adaptability of this technology is clearly reflected in the diverse segmentation of its market. The most common form factor, External Serial Device Servers, commands the largest market share due to its ease of installation and deployment flexibility, which makes it suitable for a wide range of industrial environments. In contrast, Embedded Serial Device Servers are experiencing the fastest growth as they are increasingly integrated directly into new OEM equipment, compact IoT devices, and other systems where space is at a premium. A similar dynamic is seen in port configuration; while large industrial facilities prefer Multi-Port servers to consolidate connections from numerous devices, Single-Port servers are expanding rapidly to meet the specific needs of small businesses and targeted edge applications, showcasing the technology’s broad and versatile utility across countless use cases.
A Global Imperative for Integration
The pressing need for this legacy-to-modern bridge technology is not confined to any single region but has become a truly global phenomenon, driven by universal goals of efficiency and modernization. North America currently leads the market, a position supported by its highly advanced industrial automation landscape, extensive early adoption of IoT technologies, and significant public and private investments in smart infrastructure projects. However, the Asia-Pacific region is projected to be the fastest-growing market through 2032, with its expansion fueled by rapid industrialization, ambitious government-led smart city projects, and large-scale investments in digital transformation, especially within China’s manufacturing sector. This worldwide adoption pattern underscores the universal challenge that organizations everywhere face: how to integrate proven, reliable legacy systems with the inevitable future of automation and connectivity in a way that is both secure and economically viable.
An Enduring Bridge to the Future
The Serial Device Server Market was poised for consistent and healthy growth, a trajectory built on its fundamental role in bridging legacy systems with modern digital infrastructures. Its continued relevance was ensured by the persistent priority of maintaining industrial continuity while pursuing innovation. The market’s upward momentum was further propelled by the powerful and interconnected trends of smart factory adoption, the relentless expansion of IoT networks, and a heightened global focus on industrial cybersecurity. Furthermore, ongoing innovations such as the development of cloud-enabled and advanced wireless models continued to expand the technology’s applications into new and unforeseen domains. Ultimately, as organizations across the globe sought to enhance operational efficiency and modernize their systems, the humble serial device server proved itself to be a vital and indispensable technological component.